Self-Sovereign Network
Leveraging DID and Blockchain Registry, we have established a self-sovereign peer-to-peer network using a Blockchain-Edge-Client (BEC) architecture. It eliminates the need for third-party trust, enabling direct information exchange and trustless value exchange between any two entities.
BEC architecture
The BEC framework decentralizes data storage by distributing it across the appropriate locations. It is built on three pillars:
Edge: Users store personal data (e.g., documents, chat logs, photos) on their private edge servers. All user interactions, whether with other individuals or services, are facilitated through this server. Our instantiation of this component is Terminus, the open source self-hosted operating system running on edge devices.
Blockchain: High-value data like DIDs and transactions are stored on the blockchain for transparency, security, and discoverability. Snowinning Protocol stores the DID Registry on Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) supported blockchains via smart contracts.
Client: The identity wallet app that enable users to maintain full control of their private keys stored on mobile devices. Our instantiation of this component is TermiPass, the comprehensive client app of Terminus.
Direct trustless information exchange through BEC
We’ll demonstrate the BEC network topology using Alice and Bob, who have initially registered their DIDs on the blockchain. Here are the steps when Alice sends a message to Bob through the BEC framework:
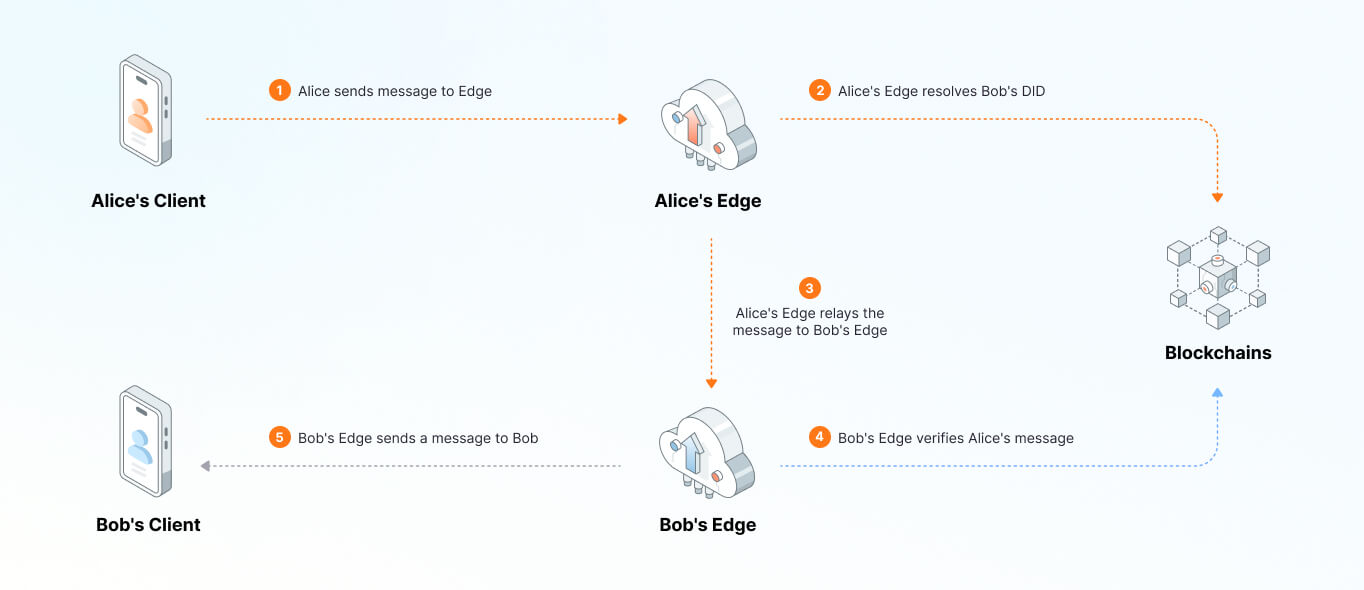
- Alice sends the message from her terminal device to her Edge server.
- Using the blockchain as a decentralized Domain Name System (DNS), Alice’s Edge determines Bob’s Edge location.
- Alice’s Edge forwards the message to Bob’s Edge.
- Bob’s Edge verifies the authenticity of the message by validating Alice’s cryptographic signature against the blockchain, similar to how a Certificate Authority (CA) functions.
- Once validated, the message is securely relayed from Bob's Edge to his terminal device.
Trustless value exchange via Otmoic
The Otmoic protocol is a trustless automatic value-exchange protocol built on the Snowinning Protocol. It is designed to provide public goods with a fair price, ensuring transparency and decentralized value exchange. Key features include:
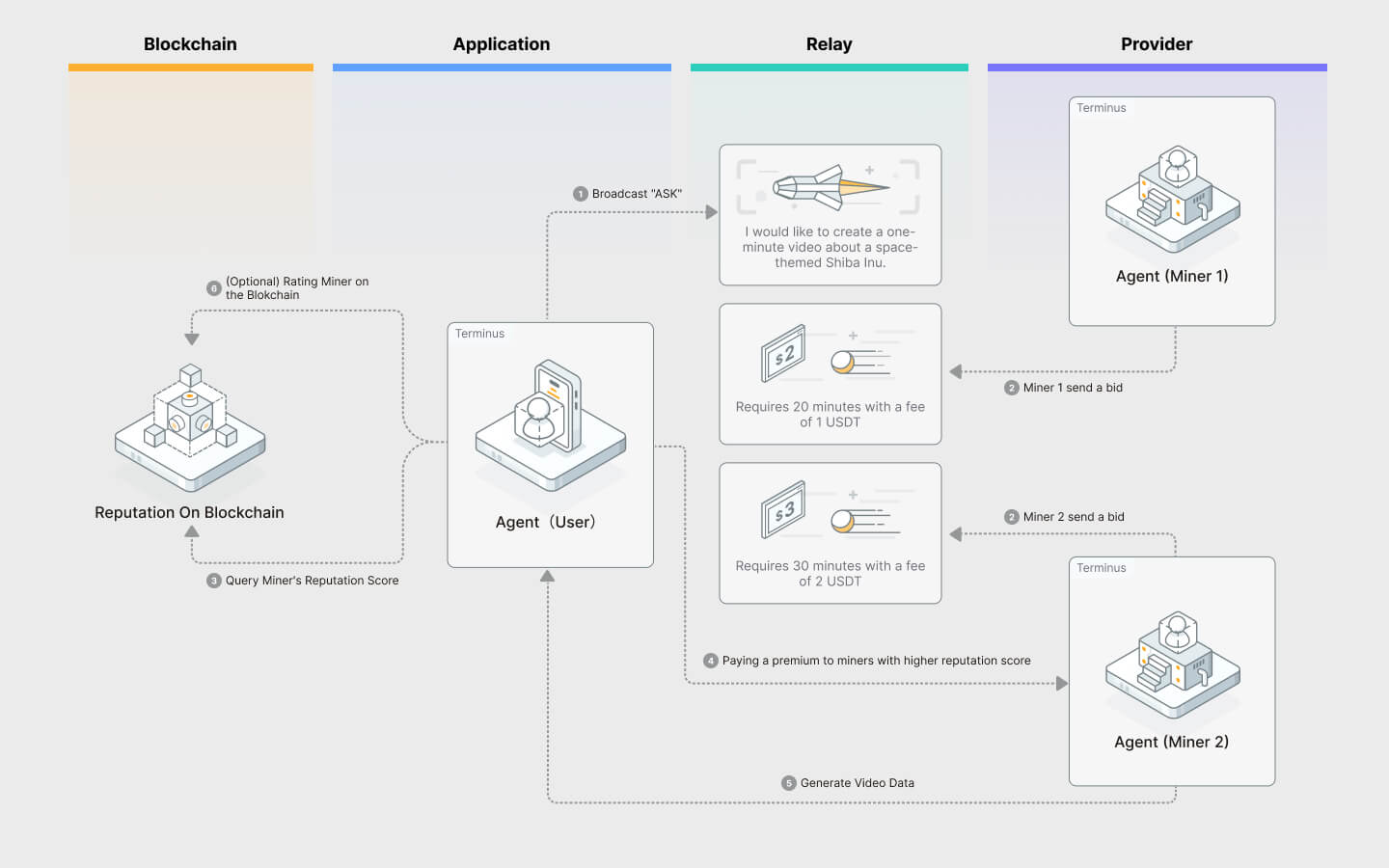
- On-chain Reputation Mechanism: Implements a reputation system for traders and liquidity providers, addressing the free mint problem.
- KYC Support via Verifiable Credentials: Ensures identity verification without compromising decentralization.
- RFQ-Based Price Discovery: Allows for efficient Request-for-Quote (RFQ) driven price discovery.
- Atomic Swap Support: Facilitates trustless, on-chain atomic swap transactions.
- Automatic Market Making: Liquidity providers can engage in automatic market-making by installing applications on Terminus.